Module 2: Debugging and Error Handling
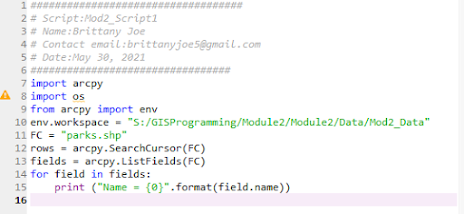
This week we learned about the types of errors in scripting and how we can utilize the debugging tool in Spyder to fix those errors. Additionally, we learned about try-except statements that allow us to run a script with exceptions. The first thing to note about errors in a script is the color separation that identifies errors in the console. Red is commonly used to identify errors. An example of what is identified as an error is a syntax error with a ^ position symbol ( this doesn't mean it is where the location of the error). Script 1 To get the results for this script, we had to fix the FC that was misspelled. I also had to update the file path and recognizing the correct function was used and entered correctly. Script 2 For the second script, we were tasked to correct the script's errors. By making changes into the file path to update and correct any spelling of the files. Additionally, correct small details of assigned features and were carried over in...





